Open enrollment is reserved for employees to make changes to their benefits elections. This yearly period allows you to change or renew your health care coverage or the upcoming calendar year. Understanding your employee benefits can feel overwhelming, especially if the vocabulary surrounding benefits is unfamiliar to you. Learning the terminology can help you feel more confident when choosing or reviewing your coverage. Use these definitions of common open enrollment terms to help you navigate your benefits options.
Open enrollment is reserved for employees to make changes to their benefits elections. This yearly period allows you to change or renew your health care coverage or the upcoming calendar year. Understanding your employee benefits can feel overwhelming, especially if the vocabulary surrounding benefits is unfamiliar to you. Learning the terminology can help you feel more confident when choosing or reviewing your coverage. Use these definitions of common open enrollment terms to help you navigate your benefits options.
Common Open Enrollment Terms
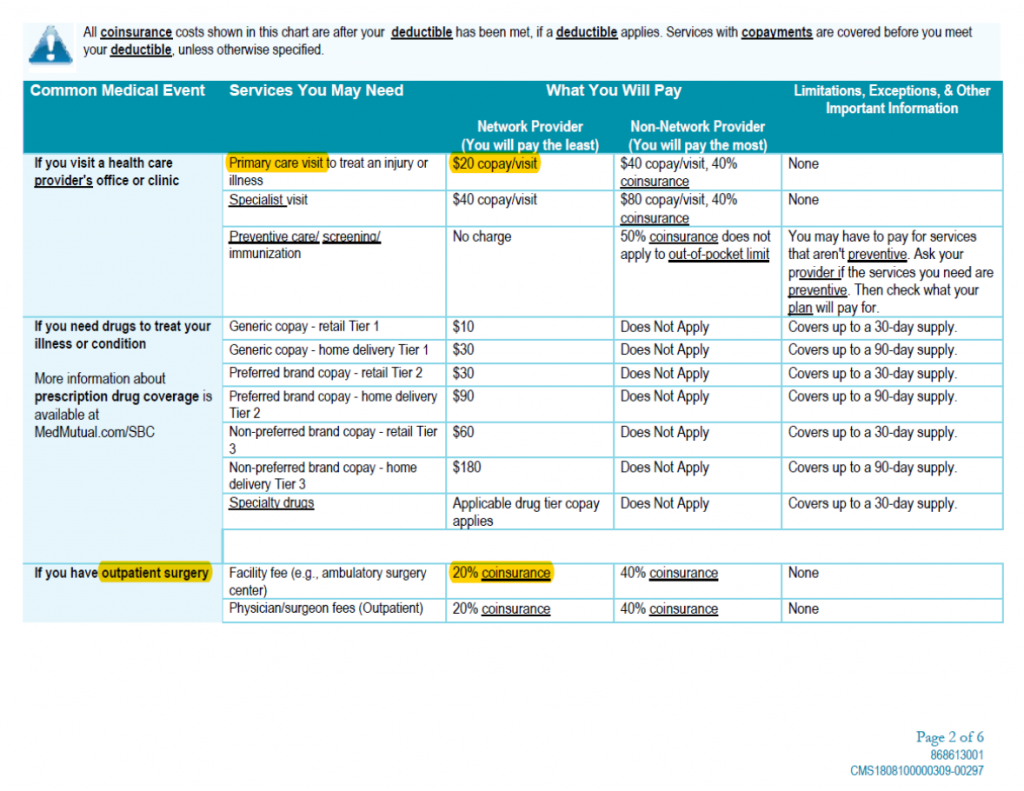
Coinsurance is the amount or percentage you pay for certain covered health care services under your health plan. This is typically the amount paid after a deductible is met, and it can vary based on the plan design.
Consumer Driven Health Care (CDHC) are health insurance programs and plans that are intended to give you more control over your health care expenses. Under CDHC plans, you can use health care services more effectively and have more control over your health care dollars. CDHC plans are designed to be more affordable because they offer reduced premium costs in exchange for higher deductibles. Health reimbursement arrangements (HRAs) and health savings accounts (HSAs) are
common examples of CDHC plans.
Copayment (copay) is a flat fee that you pay toward the cost of covered medical services.
Covered charges are health care expenses that are covered under your health plan.
Deductibles are a specific dollar amount you pay out of pocket before benefits are available through a health plan. Under some plans, the deductible is waived for certain services.
Dependents are individuals who meet eligibility requirements under a health plan and are enrolled in the plan as a qualified dependent.
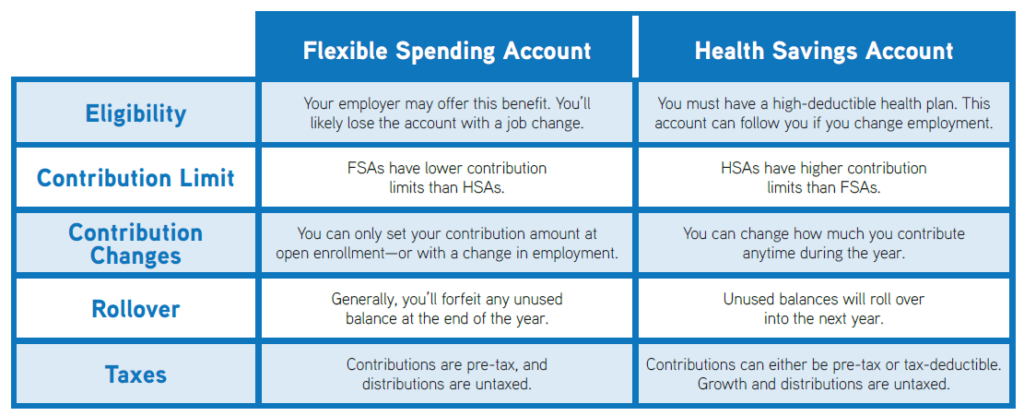
Flexible spending accounts (FSAs) are accounts that allow you to save tax-free dollars for qualified medical and/or dependent care expenses that are not reimbursed. You determine how much you want to contribute to the FSA at the beginning of the plan year. Most funds must be used by the end of the year, as there is only a limited carryover amount.
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) are types of health insurance plans that usually limit coverage to care from doctors who work for or contract within a specified network. Premiums are paid monthly, and a small copayment is due for each office visit and hospital stay. HMOs require you to select a primary care physician responsible for managing and coordinating all of your health care.
Health reimbursement arrangements (HRAs) are employer owned medical savings accounts in which the company deposits pre-tax dollars for each of its covered employees. Employees can then use this account to reimburse qualified health care expenses.
Health savings accounts (HSAs) are employee-owned medical savings accounts used to pay for eligible medical expenses. Funds contributed to the account are pre-tax and do not have to be used within a specified time period. HSAs must be coupled with qualified high deductible health plans (HDHPs).
High deductible health plans (HDHPs) are qualified health plans that combine very low monthly premiums in exchange for higher deductibles and out-of-pocket limits. These plans are often coupled with an HSA.
In-network is health care received from your primary care physician or a specialist within an outlined list of health care practitioners. Inpatient refers to a person who is treated as a registered patient in a hospital or other health care facility.
Medically necessary (or medical necessity) are services or supplies provided by a hospital, health care facility or physician that meet the following criteria: (1) are appropriate for the symptoms and diagnosis and/or treatment of the condition, illness, disease or injury; (2) serve to provide diagnosis or direct care and/or treatment of the condition, illness, disease or injury; (3) are in accordance with standards of good medical practice; (4) are not primarily serving as convenience; and (5) are considered the most appropriate care available.
Medicare is an insurance program administered by the federal government to provide health coverage to individuals aged 65 and older or who have specific disabilities or illnesses.
Members are those enrolled in a health plan. This includes eligible employees, their dependents, Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (COBRA) beneficiaries and surviving spouses.
Out-of-network is health care you receive without a physician referral or services received from a nonnetwork service provider. Out-of-network health care and plan payments are subject to deductibles and copayments.
Out-of-pocket expenses are the amount that you must pay toward the cost of health care services. This includes deductibles, copayments and coinsurance. Out-of-pocket maximums (OOPMs) are the highest out-of-pocket amount paid for covered services during a benefit period.
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs) are health plans that offer both in-network and out-of-network benefits. Members must choose one of the in-network providers or facilities to receive the highest level of benefits.
Premium is the amount you pay for a health plan in exchange for coverage. Health plans with higher deductibles typically have lower premiums.
Primary care physicians (PCPs) are doctors who are selected to coordinate treatment under your health plan. This generally includes family practice physicians, general practitioners, internists and pediatricians.
This cheat sheet does not account for every term or definition you may see during open enrollment, but it provides an overview of some of the most common ones.
If you have questions, check with your employer for further resources.




 It’s that time of year again. The leaves are changing, the temperature is getting cooler, and you’re doing everything you can to avoid the flu. No one enjoys being sick, but some of us are more prone to sickness than others. Knowing where you are most likely to come into contact with germs and what you can do to prevent sickness are key for this fall season.
It’s that time of year again. The leaves are changing, the temperature is getting cooler, and you’re doing everything you can to avoid the flu. No one enjoys being sick, but some of us are more prone to sickness than others. Knowing where you are most likely to come into contact with germs and what you can do to prevent sickness are key for this fall season.